Sinus infection (sinusitis): Symptoms, causes & treatment
Find an ENT specialistSinus infections can leave you feeling miserable. You may experience facial pain, congestion, headaches or pressure around your eyes and nose.
Most sinus infections go away on their own. However, if your symptoms last longer than 10 days without improvement or you have a fever, it’s a good idea to be seen by an ear, nose and throat specialist.
Need care now? Try telehealth
Symptom Checker can help you find the right type of care based on your symptoms. From 24/7 urgent care video visits to e-visits, we’ll recommend the best visit for you. Try Symptom Checker in LiveWell.
What is a sinus infection?
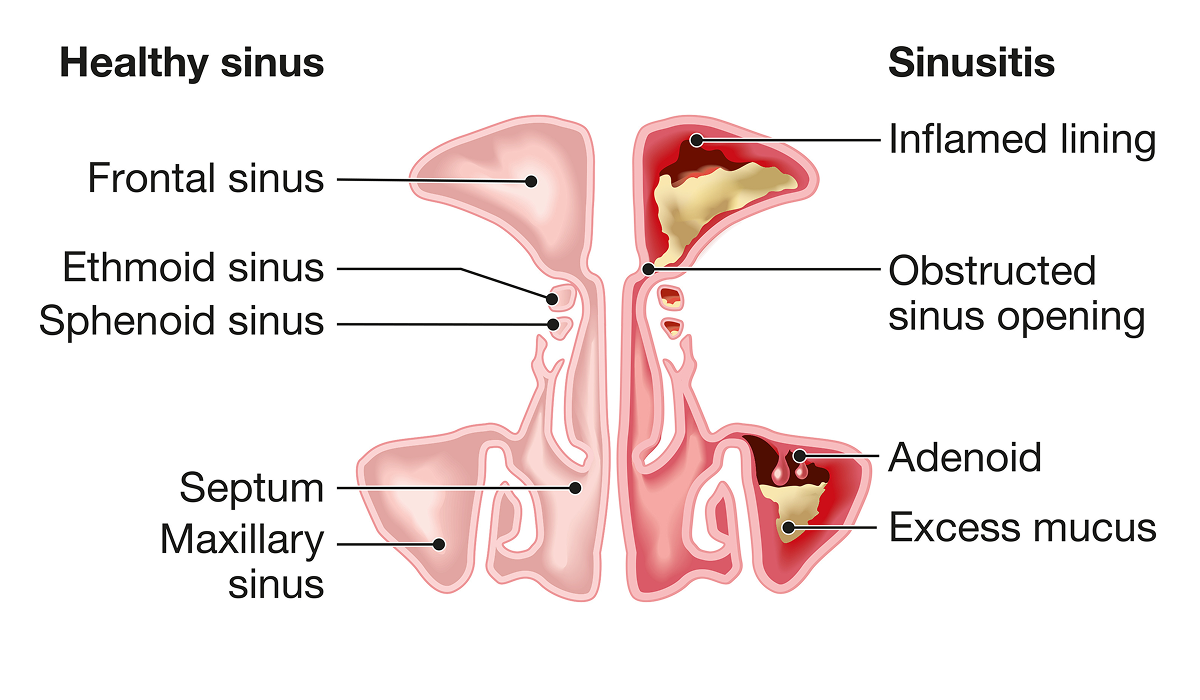
When the sinus is affected by sinusitis, inflammation, mucus buildup and blocked sinus openings can result.
A sinus infection, also known as sinusitis or rhinosinusitis, happens when your nasal cavities become swollen and inflamed. This inflammation can block mucus from draining, creating a breeding ground for viruses, bacteria or fungi to grow.
There are two types of sinus infections – acute (short term) or chronic (lasting more than 12 weeks).
Sinus infection symptoms
Sinus infections can mimic other upper respiratory infections, but there are some key signs of a sinus infection:
- Facial pain or pressure
- Headache
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Postnasal drip
- Cough, especially at night
- Loss of smell or taste
- Fatigue
- Fever (more common with bacterial infections)
- Bad breath
Acute sinusitis symptoms often develop suddenly and improve within 10 days. Chronic sinusitis symptoms may linger and feel less intense but more persistent.
What causes sinus infections?
Sinus infections develop for a variety of reasons. Upper respiratory infections and severe allergies can even cause sinus infections.
Common sinus infection causes include:
- Viral infections: This is often the result of a cold or upper respiratory infection.
- Bacterial infections: May occur if a viral infection doesn’t clear up.
- Fungal infections: More likely to occur in people with weakened immune systems or with chronic sinus issues.
- Allergies: Inflammation from allergies can block the sinuses.
- Nasal polyps or structural problems: Issues such as a deviated septum can trap mucus and increase your risk.
- Environment: Seasonal changes, smoking or air pollution may contribute to sinusitis.
Are sinus infections contagious?
Viral sinus infections are the most common type and can spread from person to person, just like a cold. If your infection starts with a virus, you may be contagious for a few days, especially during the early stages when symptoms such as sneezing and coughing are present.
Bacterial sinus infections, on the other hand, typically aren't contagious. They often develop when a viral infection doesn't fully clear, and bacteria start to grow in the inflamed sinuses. These types of infections are less likely to spread to others.
What’s the best way to tell the difference? If you have a fever, you’re more likely to be contagious.
To reduce your risk of spreading or catching a sinus infection:
- Wash your hands frequently.
- Avoid close contact with others who are sick.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Disinfect shared surfaces regularly.
Diagnosing sinus infections
If you suspect you have a sinus infection, you can consult your doctor or get immediate care with an e-visit or urgent care video visit.
If you require an in-person visit with your doctor, they’ll check for swelling, tenderness and nasal discharge and may use a nasal endoscopy to view your sinuses. If you get regular sinus infections, your doctor may order an allergy test to check for any allergies.
Sinus infection treatment
Most sinus infections caused by viruses go away on their own within 10 days. But if symptoms persist or worsen, treatment can help you feel better faster.
Common treatments for sinus infections include over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers, decongestants, saline nasal sprays and humidifiers.
If your sinus infection is severe, your doctor may recommend antibiotics for bacterial infections, corticosteroid nasal sprays to reduce inflammation or antihistamines for allergy-related sinusitis.
In cases of chronic sinusitis or structural problems, endoscopic sinus surgery may be needed to open nasal passages.
In addition to medications, you can support recovery at home by:
- Resting and staying hydrated
- Using a warm compress to ease facial pain
- Gently rinsing your nasal passages with a saline solution
- Avoiding irritants like smoke or strong fragrances
If your symptoms last longer than expected, don’t hesitate to reach out to an ENT specialist or your primary care provider.
Get care
We help you live well. And we’re here for you in person and online.